SMALP 200
The SMALP, among all synthetic nanodisc products has been developed for for the solubilization of membrane proteins from all kinds of cell membranes and subsequent isolation & purification of said membrane proteins. After dissolving SMALP 200 + buffer powder in dH2O, the product is ready-to-use. SMALP 200 has a yellowish color in solution. After successfull solubilization of the membrane protein, the protein can be purified using affinity chromatography. For membrane protein purification we recommed to use the Rho1D4-tag. Cube Biotech offers the matching products for this purpose.
SMALP Screening: Different membrane protein usually perform different under different SMAs variants respectively. To ease the resulting screening process we compiled all of our SMAs into a convenient SMALP Screening Set. Furthermore if you like to compare proteins's performance between SMA and DIBMA in synthetic nanodiscs, we also offer our, that includes both our SMA and DIBMA products.

Figure 1: Western Blot of a purified membrane protein after stabilization through SMA. Reproduced with permission from Ms S. Nestorow, University of Birmingham.
FEATURE | |
State | Lyophilized Powder, to be solved with water |
Polymer styrene-to-maleic anhydride ratio | 2:1 |
Molecular weight | 6,500 Da |
pH after solving | 7.5 |
Solubility | 40 % |
Divalent cationic tolerance | < 5 mM |
Color | Yellowish |
Odor | Odorless |
Freeze-thaw stable? | Yes |
Storage | 4°C for long-term |
Other noteworthy feature | Most commonly used SMA |
Structure | 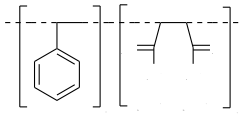 |
Order number | Products | Shipment Temperature | Storage Temperature |
18210 | SMALP 200 10x50 mg | Ambient temperature | -20°C |
18211 | SMALP 200 1 g | Ambient temperature | -20°C |
18212 | SMALP 200 10 g | Ambient temperature | -20°C |
如需咨询或订购 中国独家总代理: 成都正民德思生物科技有限公司 www.zenmindes.com
请拨打 400-9910-165 / 028-85568133
或添加微信 zenmindes-sale
 咨询
咨询
Noh I., Guo Z., Zhou J., Gao W., Fang R.H., Zhang L.
Univerzita Karlova Přírodovědecká fakulta.
Hernandez L.M.R. & Levental I.
sciencedirect.
Zhou R., Zhang S., Nguyen H.T., Ding H., Gaffney A., Kappes J.C.,Smith Ill A.B.S, Sodroski J.G.
bioRxiv.












 首页
首页